Understanding the Bullwhip Effect in Demand Planning

By Intelichain’s Team
The Bullwhip Effect refers to the magnification of demand variability as orders move upstream from consumers to manufacturers in the supply chain. A small change in retail demand can cause progressively larger changes in orders at the wholesale, distributor, manufacturer, and raw material supplier levels. This creates a “whip-like” effect where minor demand changes become exaggerated, leading to significant supply chain disruptions.
Causes of the Bullwhip Effect
- Demand Forecasting: Inaccurate or overly responsive demand forecasts can cause significant order variability. When companies rely on these forecasts to make inventory decisions, even small errors can amplify up the supply chain.
- Order Batching: Companies often place orders in batches to take advantage of bulk purchasing discounts or to meet production schedules. This batching can cause demand spikes and lulls, contributing to the Bullwhip Effect.
- Price Fluctuations: Promotional discounts, price changes, and other financial incentives can lead to erratic purchasing behavior. Customers may buy in bulk during sales periods, causing sudden demand spikes.
- Lead Time Variability: Longer lead times increase the uncertainty of demand, leading companies to order more stock as a buffer. This increases inventory levels and amplifies demand variability.
- Supply Chain Coordination: Lack of coordination and information sharing among supply chain partners leads to independent decision-making, which can exacerbate the Bullwhip Effect. Each tier in the supply chain reacts to demand changes without considering the entire chain’s needs.
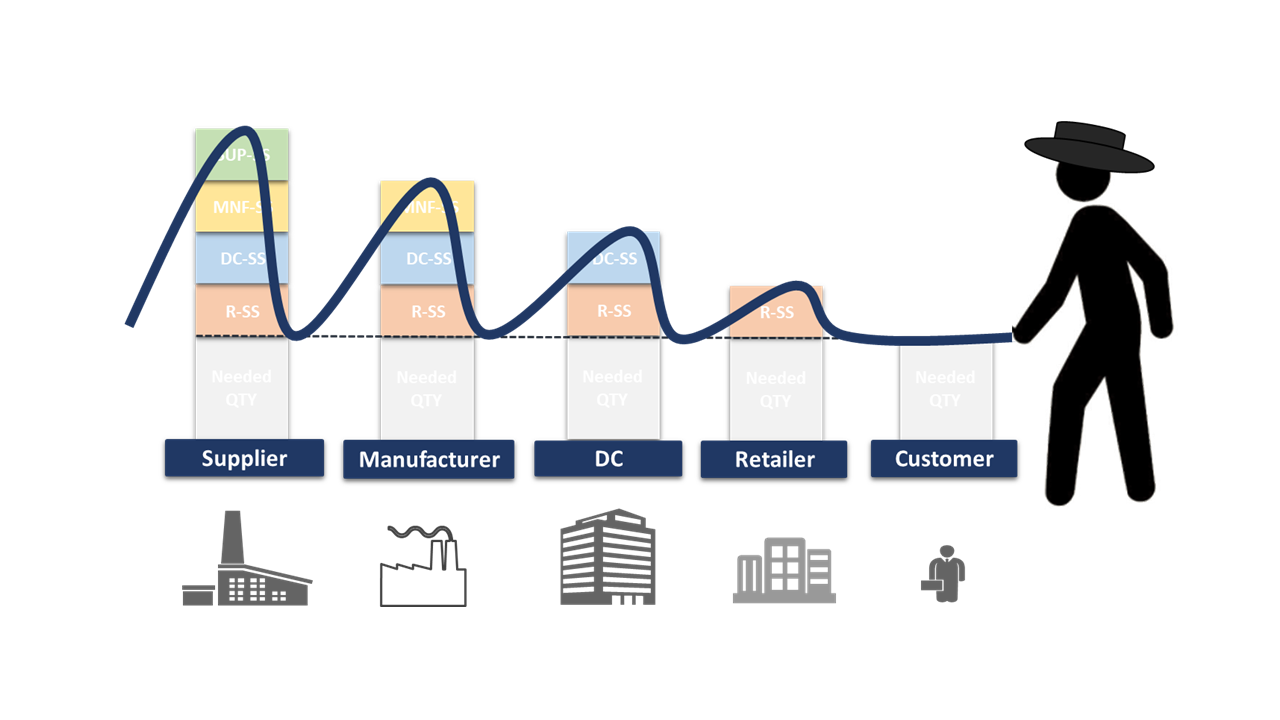
Impacts of the Bullwhip Effect
- Excess Inventory: Companies may overstock inventory to buffer against perceived demand increases, leading to higher holding costs and potential waste.
- Stockouts: Conversely, companies may also face stockouts if they underestimate demand, resulting in lost sales and dissatisfied customers.
- Increased Costs: Fluctuations in orders can lead to higher production and transportation costs as companies rush to meet demand spikes or scale back during demand lulls.
- Reduced Service Levels: Erratic demand patterns make it challenging to maintain consistent service levels, impacting customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Operational Inefficiency: The Bullwhip Effect creates operational inefficiencies, such as frequent changes in production schedules, increased labor costs, and suboptimal resource utilization.
The Bullwhip Effect poses significant challenges in demand planning and supply chain management. Understanding its causes and impacts is the first step towards developing effective strategies to mitigate its effects. By improving demand forecasting, smoothing orders, stabilizing prices, reducing lead times, enhancing supply chain coordination, and implementing agile practices, companies can minimize the Bullwhip Effect and achieve a more efficient and responsive supply chain. Addressing this phenomenon is crucial for maintaining optimal inventory levels, reducing costs, and delivering superior customer service.