Coefficient of Variation (CoV) vs. Forecastability in Demand Planning

By Intelichain’s Team
Understanding the variability and predictability of demand is crucial for accurate forecasting. Two key concepts that play a significant role in this context are the Coefficient of Variation (CoV) and Forecastability.
Understanding Coefficient of Variation (CoV)
The Coefficient of Variation (CoV) is a statistical measure of the relative variability of a data set. It is defined as the ratio of the standard deviation to the mean, and it is often expressed as a percentage. The CoV is particularly useful in comparing the degree of variation between different data sets, regardless of their units of measurement.
Formula:
where:
- σ is the standard deviation
- μ is the mean
Importance of CoV in Demand Planning
- Assessing Demand Variability: CoV provides a clear picture of demand variability. A high CoV indicates high variability, suggesting that demand is less predictable and more challenging to manually forecast accurately. Conversely, a low CoV indicates stable demand with less variability.
- Inventory Management: Products with high CoV may require higher safety stock levels to buffer against unpredictable demand fluctuations, whereas products with low CoV can be managed with leaner inventory levels.
- Resource Allocation: Understanding the CoV helps in prioritizing resources. Products with lower CoV can be forecasted with simpler models, freeing up resources to focus on more complex, variable products.
Forecastability
Forecastability refers to the ease with which future demand can be predicted accurately. It is influenced by several factors, including demand patterns, historical data quality, market conditions, and external influences such as economic shifts or seasonal trends.
Key Factors Influencing Forecastability:
- Historical Data Quality: Accurate and comprehensive historical data improves forecastability. Poor-quality data leads to unreliable forecasts.
- Demand Patterns: Regular and stable demand patterns are easier to forecast than erratic or sporadic demand.
- Market Conditions: Stable market conditions enhance forecastability, while volatile markets introduce uncertainties that complicate forecasting.
- External Influences: Factors such as economic conditions, regulatory changes, and competitor actions can significantly impact forecastability.
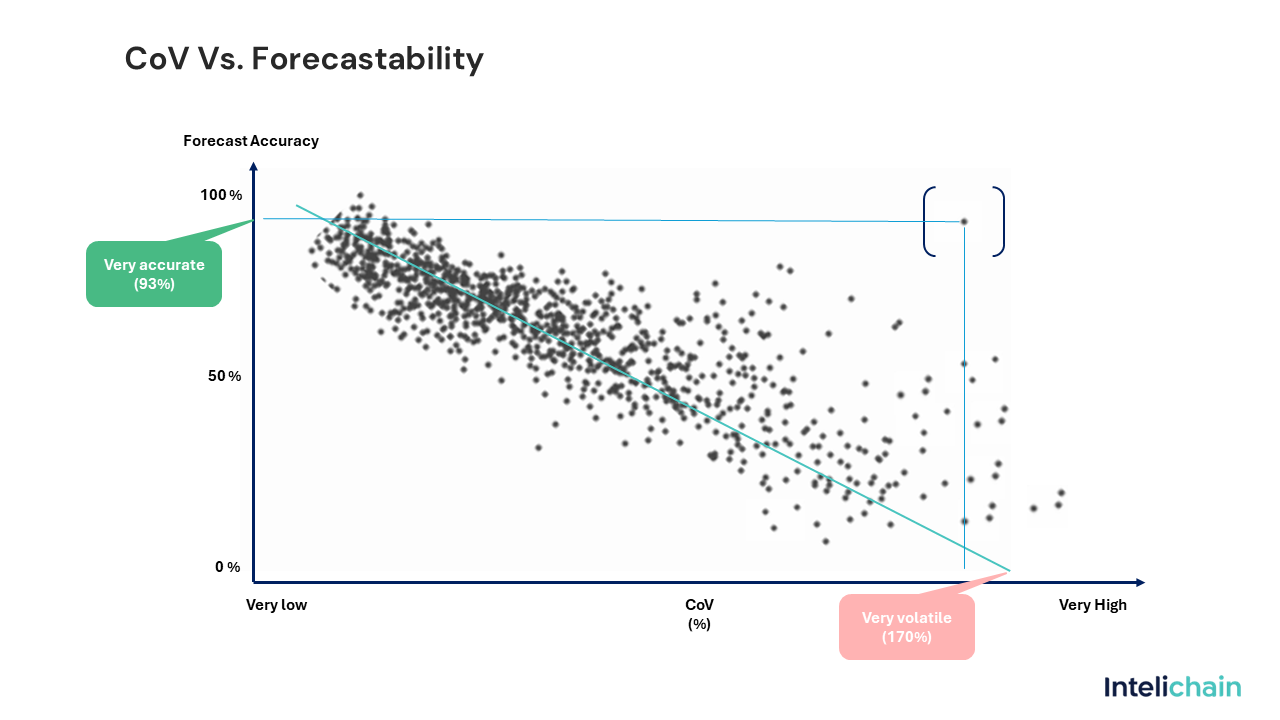
CoV vs. Forecastability
The Coefficient of Variation (CoV) and Forecastability are closely interrelated. CoV is a quantitative measure that directly impacts the qualitative aspect of forecastability.
- High CoV and Low Forecastability: Products with a high CoV exhibit high variability, making them less forecastable. These products require more sophisticated forecasting models.
- Low CoV and High Forecastability: Products with a low CoV have stable demand patterns, making them highly forecastable. Simple forecasting models can be effectively used for these products, and inventory levels can be optimized without significant risk of stockouts.
- Segmentation for Strategy Development: By segmenting products based on their CoV, companies can develop tailored forecasting and inventory management strategies. High CoV products may require advanced analytics and robust demand planning processes, while low CoV products can be managed with more straightforward approaches.
Understanding the Coefficient of Variation (CoV) and Forecastability is essential for effective demand planning. CoV provides a quantitative measure of demand variability, which directly impacts the forecastability of products. By leveraging these concepts, organizations can develop tailored strategies to enhance forecasting accuracy, optimize inventory management, and improve overall supply chain efficiency.