Introduction
In spare parts management, certain components are used very rarely, yet their availability is critical. The Poisson model is ideal for forecasting such rare events, providing a statistically grounded approach to service-level planning and inventory control.
Understanding the Poisson Model
The Poisson model predicts the number of events (demand occurrences) in a fixed period based on historical averages. The probability of observing kk events is given by:
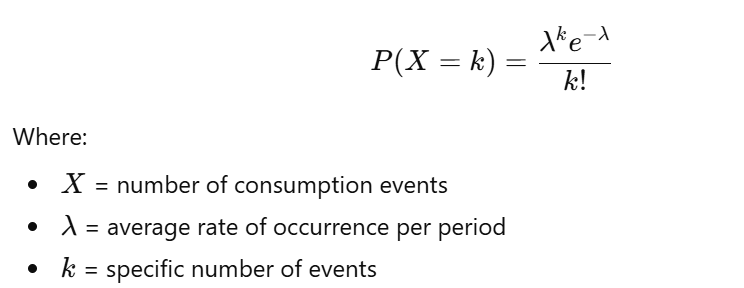
Applications in Spare Parts
-
Service level optimization: Determines the probability of fulfilling demand without stockouts.
-
Reorder point calculation: Defines inventory thresholds to trigger replenishment.
-
Inventory planning for critical parts: Ideal for emergency or backup components with unpredictable usage.
Advantages
-
Simple, yet powerful for low-frequency demand items.
-
Provides quantifiable risk of stockouts, supporting service-level agreements.
-
Scales easily across a large portfolio of rare-use components.
Implementation Tips
-
Use a rolling window of historical data to estimate λ\lambda.
-
Adjust for seasonal variations if spare parts usage fluctuates cyclically.
-
Combine with safety stock calculations for optimal replenishment.





